Caffeine: a beloved morning companion for many and a crucial ingredient in our daily pick-me-up. But how much do we really know about this popular stimulant? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of caffeine and explore “how caffeine affects your body”, from its natural sources and effects on the body to the benefits and potential dangers of its consumption. Prepare to embark on a fascinating journey that will change the way you view your daily cup of coffee, as we discuss how caffeine affects your body.
Key Takeaways
- Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant that can lead to alertness but should be consumed in moderation.
- Consuming moderate amounts of caffeine has been linked to improved focus and cognitive function, as well as reduced risk of certain diseases.
- Excessive consumption may have negative side effects such as high blood pressure, heightened anxiety or difficulty sleeping. Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should limit intake for safety reasons.
Understanding Caffeine: A Central Nervous System Stimulant

Caffeine, a central nervous system stimulant, is naturally present in several plants and added to certain foods, drinks, and medications.
Adenosine is a chemical present in all cells of the body. In the brain, it acts as a central nervous system depressant, and promotes sleep.
Caffiene works by inhibiting adenosine receptors in the brain, leading to heightened alertness and diminished fatigue.
However, one should consider the potential adverse effects, such as:
- increased acidity in the stomach, leading to conditions like heartburn or gastric distress
- increased heart rate and blood pressure
- difficulty sleeping or insomnia
- jitteriness or anxiety
- dehydration
Individual sensitivity to caffeine effects varies; hence, understanding your personal tolerance level is vital.
Natural Sources of Caffeine
Caffiene is commonly found in coffee, tea, chocolate, and energy drinks. Sources include coffee beans, tea leaves, cocoa beans, and kola nuts.
The caffeine content in coffee can be influenced by factors such as the type of bean, the darkness of the roast, fineness of the beans when ground, and the duration of the brewing process.
How Caffeine Acts in the Body
Caffeine operates by obstructing adenosine receptors in the brain, resulting in heightened alertness and decreased fatigue. Its effects peak between 30 to 60 minutes after consumption and can persist in one’s system for numerous hours, or even a few days for individuals who are especially sensitive to it.
Avoiding caffeine at least six hours before bedtime is advisable for a restful night’s sleep.
Caffiene also has a diuretic effect on the bladder, increasing blood flow the kidneys and smooth muscle of the bladder, causing increased frequency and urgency in urination.
The Positive Effects of Caffeine on the Body

Caffeine boasts a variety of positive effects, such as improved focus, enhanced cognitive function, and potential health benefits, all of which can be attributed to caffeine’s effects.
Exploring these benefits further, we can see how moderate caffeine consumption can be advantageous.
Alertness and Focus
Caffeine has been shown to have several benefits, including:
- Increasing alertness and concentration
- Enhancing visual focus
- Improving impulse control
- Boosting attention and mental alertness
These effects make caffeine a widely accepted means of combating fatigue.
Yet, over-consumption of caffeine can trigger jitteriness, anxiety, and insomnia. Striking a balance and adhering to the recommended guidelines for healthy adults is key.
Cognitive Function
Research has indicated that caffeine may enhance memory, reaction time, and decision-making, contributing to improved cognitive function overall. Additionally, regular coffee intake has been associated with a decreased risk of developing Alzheimer’s, dementia, and a 45 percent reduction in suicide risk.
This promising evidence suggests that caffeine may play a protective role against cognitive decline and certain diseases, making it an appealing choice for many individuals.
Health Benefits
In addition to cognitive advantages, moderate caffeine consumption has been linked to:
- a reduced risk of Parkinson’s disease, dementia, and some cancers
- elevated energy levels
- mitigated risk of type 2 diabetes
- sustained brain health
- promoted weight management
- augmented overall health.
It’s worth noting, though, that these benefits usually coincide with moderate caffeine intake, and excessive consumption can have negative side effects.
Negative Side Effects of Excessive Caffeine Intake
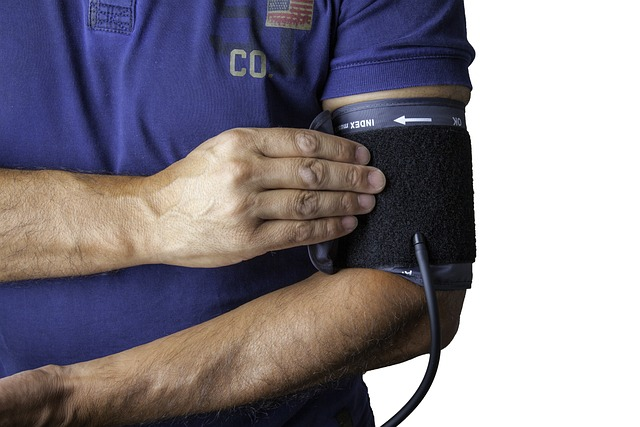
While caffeine has numerous benefits, potential negative side effects associated with over-consumption should not be overlooked. These may include elevated blood pressure, increased levels of anxiety, and disturbed sleep.
Blood Pressure and Heart Health
Caffeine may cause a brief but marked rise in blood pressure, even in individuals with normal blood pressure. It can also lead to an altered heart rhythm, although moderate caffeine consumption is unlikely to have adverse effects on heart health.
It is recommended that individuals with high blood pressure, hypertension, or heart-related problems consult their doctor to determine whether or not caffeine consumption is safe.
Anxiety and Mood
Too much caffeine can lead to increased anxiety, irritability, and mood swings. It has been observed that caffeine can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and impede sleep, potentially contributing to feelings of depression.
To avoid these negative effects, it’s important to monitor and moderate caffeine intake.
Sleep Quality
Consuming too much caffeine, especially close to bedtime, can negatively impact sleep quality and duration. Caffeine consumption can:
- Reduce the time it takes to fall asleep
- Decrease the total amount of sleep attained
- Lower the proportion of deep sleep obtained, which is essential for feeling rejuvenated and invigorated.
For maintaining healthy sleep patterns, strategies like gradually cutting down on caffeine intake, stop consuming caffeine, and refraining from that evening cup of coffee are worth considering.
Caffeine Consumption Guidelines for Healthy Adults

For maximizing caffeine benefits while minimizing potential risks, healthy adults should adhere to safe consumption guidelines and consider individual tolerance levels.
Daily Limits
Many people wonder how much caffeine they can consume daily. The recommended daily limit for caffeine intake is up to 400 milligrams of caffeine for most healthy adults, equivalent to approximately four or five cups of coffee. Consuming caffeine within this limit can help avoid potential adverse effects on health and well-being.
Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase alertness, focus, and energy levels when otherwise healthy people consume caffeine within the recommended intake.
Individual Tolerance
Since individual sensitivity to caffeine varies, it’s crucial to pay attention to your body’s responses and adjust your intake accordingly. Factors such as:
- age
- gender
- body weight
- genetics
Factors such as genetics, age, and frequency of ingested caffeine can all influence how quickly a person develops a tolerance to caffeine, especially when consuming more caffeine than usual.
By being mindful of one’s body and adjusting how much caffeine you drink, as needed, individuals can enjoy the benefits of caffeine while minimizing potential risks.
Special Considerations for Caffeine Intake

Certain populations should avoid caffeine and exercise caution with their caffeine intake, including pregnant and breastfeeding individuals and those with specific medical conditions or taking certain medications.
These special considerations help ensure that caffeine consumption remains safe and beneficial for all individuals.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should limit caffeine intake to 200-300mg per day to reduce potential risks to the fetus or infant.
This recommended limit is approximately equivalent to one 8-oz cup of coffee per day during pregnancy.
Medical Conditions and Medications
For those with medical conditions or taking medications that might interact with caffeine, consulting a healthcare provider before consuming caffeine is highly recommended.
By discussing your individual situation with a professional, you can make informed decisions about caffeine consumption and ensure that it remains a safe and beneficial part of your daily routine.
Caffeine Withdrawal: What to Expect

Caffeine withdrawal is the physiological response to reducing caffiene intake after having it regularly for some time. This can cause various symptoms, which can be managed by more gradually reducing intake over time.
Symptoms of Withdrawal
Symptoms of caffeine withdrawal may include:
- headaches
- fatigue
- irritability
- muscle aches
Withdrawal symptoms typically last a few days to a week, and can be minimized by slowly decreasing caffeine consumption. This gradual reduction allows the body to adjust to lower caffeine levels, helping to minimize discomfort and potential health risks.
Drinking plenty of water and getting adequate rest are effective strategies for managing caffeine withdrawal symptoms. Over the counter pain relievers can also reduce some of the symptoms, but be aware that some pain relievers advertised specifically for migraine can containe caffiene. Taking these pain relievers will work, but will counteract your efforts if you are intentionally trying to reduce caffiene dependence.
Caffeine and Athletic Performance

The effects of caffeine on athletic performance are mixed and highly individual, with some evidence suggesting potential benefits. Studies have demonstrated that caffeine can reduce fatigue, improve reaction time, and increase endurance in both aerobic and high-intensity exercises.
However, since optimal dosage and effects can differ among individuals, it’s important to take personal factors into account when determining caffeine intake for athletic performance.
Energy Drinks and Their Risks
Energy drinks can pose risks due to their high caffeine and sugar content. Mixing energy drinks with alcohol can lead to dangerous consequences, as the stimulating effects of caffeine can mask the depressant action of alcohol, impairing one’s perception of their level of intoxication, resulting in an increased likelihood of making unwise decisions.
The popularity of energy drinks among teenagers, and even adolescents, is at an all time high. Teens should be encouraged to consume energy drinks in moderation because they have varying caffiene content and it can be easy to consume more than intended, or is recommended.
Teens and adolescents experience the same increase in heart rate and blood pressure, with the potential for jitters and insomnia, both increased at higher doses. They can experience withdrawal symptoms including irritability, headache, and depression. With the increased diagnoses of mental health issues among teens, the withdrawal symptoms can be particularly concerning, so be aware of the amount of caffeine in the drinks your teen is choosing.
Being mindful of the potential dangers linked to energy drinks and practicing moderate consumption is crucial to avoid these risks.
Summary
In summary, caffeine is a powerful stimulant that can provide numerous benefits when consumed in moderation. From improved focus and cognitive function to potential health advantages, caffeine has benefits. However, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with too much caffeine consumption, such as increased blood pressure, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
It’s crucial to follow recommended guidelines for caffeine consumption and take individual tolerance levels into account. By doing so, you can enjoy the many benefits of caffeine while minimizing potential risks, making it a safe and enjoyable part of your daily routine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 5 negative effects of caffeine?
Caffeine can have a range of negative effects if consumed in excess, such as restlessness, insomnia, headaches, dizziness, fast heart rate, dehydration, anxiety, and dependency. It is possibly unsafe to consume more than 400 mg daily and can cause further side effects such as nausea, increased heart rate, chest pain, and more.
What are the long-term effects of caffeine?
Consuming too much caffeine (1000 mg or more) on a regular basis may be linked to fertility issues, sleep problems, anxiety, increased episodes of heartburn, changes in bowel habits, bone thinning and fractures, and elevated blood pressure.
How long does it take for caffeine to wear off?
Caffeine's half-life is usually between four to six hours, meaning that it takes up to 10 hours for the substance to completely leave your system. You may start to feel the effects of caffeine within 15 minutes, with its levels peaking an hour later and remaining there for several hours before slowly decreasing.
What is the recommended daily limit for caffeine intake for healthy adults?
Healthy adults should limit their daily caffeine intake to 400mg, which is approximately 4-5 cups of coffee. Children and teens 18 years and below should limit caffiene consumption to less than 100 mg according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
How can I reduce the negative effects of caffeine on sleep quality?
To reduce the negative effects of caffeine on sleep quality, try reducing your intake and avoid caffeine containing products late in the day.

